Access the essential membership for Modern Managers
Have you ever worked on a project with a tight-but-achievable deadline, where your unique knowledge and skills were vital for a successful result? Even though you found it challenging, you may well have done some of your very best work.
Or, think back to a task where you felt little pressure to deliver. The deadline may have been flexible, or perhaps the work wasn't challenging. Chances are, you did an average job at best.
There's a subtle relationship between pressure and performance. When people experience the right amount of pressure, they often perform brilliantly. However, if there's too much or too little pressure, performance can suffer.
In this article, you'll learn how the Inverted-U Theory – also known as the Yerkes-Dodson Law – can help you to understand the relationship between pressure and performance. The result will be that you'll get the best from a happy and engaged team!
Click here to watch our video on the Inverted-U Theory/Yerkes-Dodson Law.
What Is the Inverted-U Theory?
The Inverted-U Theory was created by psychologists Robert Yerkes and John Dodson in 1908. Despite its age, it's a model that has stood the test of time. [1]
The theory describes a clear relationship between pressure and performance. In the original research, pressure was exerted by electric shocks – to motivate rats to escape from a maze!
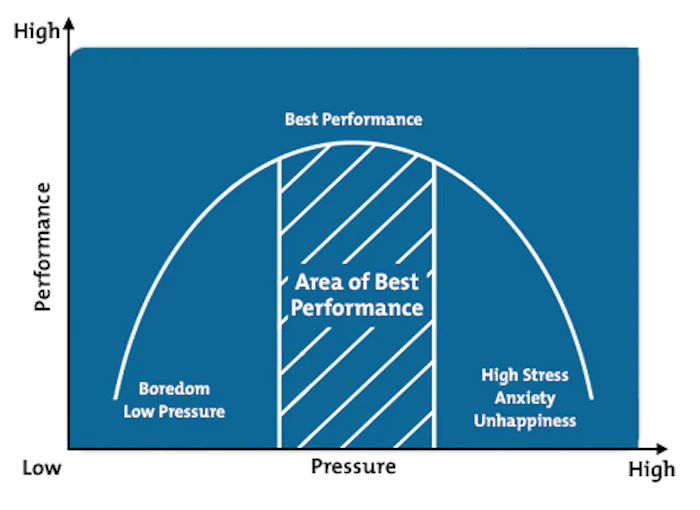
The Inverted-U Theory gets its name from the curve created when the correlation between pressure (or "arousal") and performance is shown on a graph. See figure 1, below.
Figure 1: The Inverted-U Curve.
Use the right pressure to achieve your personal best!
From "The Relation of Strength of Stimulus to Rapidity of Habit‐Formation" by Robert Yerkes and John Dodson. Published in the Journal of Comparative Neurology (1908). Work now in the public domain.
According to Yerkes and Dodson, peak performance is achieved when the level of pressure we experience is appropriate for the work we're doing. When we're under too much or too little pressure, performance declines, sometimes severely.
Understanding the Inverted-U Curve
The left hand side of the graph, above, shows the situation where people aren't being challenged. Here, they see no reason to work hard at a task, or they're in danger of approaching their work in a "sloppy," unmotivated way.
The middle of the graph shows where people work at peak effectiveness. They're sufficiently motivated to work hard, but they're not so overloaded that they're starting to struggle. This is where people can experience "flow," the enjoyable and highly productive state in which they can do their best work. (For more on this, see our article, The Flow Model.)
The right hand side of the graph shows where they're starting to fall apart under pressure. They're overwhelmed by the volume and scale of competing demands on their attention, and feeling a serious lack of control over their situation. They may exhibit signs of hurry sickness, stress, or out-and-out panic.
Note:
In reality, the exact shape of the curve will depend on both the individual and their situation. It's also important to recognize that seemingly small changes in professional or personal life can lead to rapid repositioning on the curve.
What's the Difference Between Pressure and Stress?
The Inverted-U Theory shows that pressure can be positive – up to a point. Stress, however, is never positive, and it's important not to confuse the two ideas.
When the levels of pressure we're experiencing are right for the work we're doing, we're stimulated in a beneficial way: motivated, engaged, and excited about doing our best. But stress happens when people feel out of control, and it's a wholly negative thing.
The Inverted-U Theory is about using pressure wisely, always aware of where the benefits end and stress begins.
For more information about how to identify and manage stress, see our article, Minimizing Workplace Stress.
Tip:
You can take steps to manage the way you experience pressure by using techniques such as Relaxation Imagery, Centering, and Deep Breathing. You can also use Affirmations to maintain a positive outlook and control. Consider teaching these techniques to your teams, too – though you'll also need to have the right organizational processes in place to ensure that pressure levels remain beneficial.
The Four Influencers of the Inverted-U Theory
The impact of pressure can be complex. But four key factors, or "influencers," affect how the Inverted-U Theory plays out in practice*:
- Skill Level.
- Personality.
- Trait Anxiety.
- Task Complexity.
1. Skill Level
Someone's level of skill with a given task will directly influence their performance, in terms of both their attitude and their results.
For a while, a new task is likely to be challenging enough. Later, if it starts to feel too easy, some form of extra pressure might be needed to help the person re-engage with their role.
Note:
Don't worry about people becoming too skilled or too confident. You can use the other influencers to balance this, so that they feel the optimum amount of positive pressure. Increased skill and confidence can only bring benefits to individuals and organizations.
2. Personality
A person's personality also affects how well they perform.
For instance, some psychologists believe that people who are extroverts are likely to perform better in high-pressure situations. People with an introverted personality, on the other hand, may perform better with less pressure.
The Inverted-U Theory prompts us to match our own personalities – and those of our people – to appropriate tasks. Observation, detailed knowledge of individuals, and open communication, are all important when we're allocating roles and responsibilities.
Note:
Although not addressed directly within the Inverted-U Theory, it's important to remember that people can experience various forms of personal pressure (from their family lives, for instance, or from underlying concerns about their role or organization). Try to bear these pressures in mind when setting deadlines and allocating tasks.
3. Trait Anxiety
Think of trait anxiety as the level of a person's "self-talk." People who are self-confident are more likely to perform better under pressure. This is because their self-talk is under control, which means that they can stay "in flow," and they can concentrate fully on the situation at hand.
By contrast, people who criticize or question themselves are likely to be distracted by their self-talk, which can cause them to lose focus in more challenging situations.
The more that people are able to lower their anxiety about a task (with practice, or with positive thinking, for example) the better they'll perform.
4. Task Complexity
Task complexity describes the level of attention and effort that people have to put into a task in order to complete it successfully. People can perform simple activities under quite high levels of pressure, while complex activities are better carried out in a calm, low-pressure environment.
But even when someone's skill levels are high, they may still benefit from a calm environment in which to carry out their most complex work. Conversely, people carrying out low-complexity tasks may need extra stimulation in order to feel motivated and achieve their potential.
Using the Inverted-U Theory
The simplest way to use the Inverted-U Theory is to be aware of it when you allocate tasks and projects to people on your team, and when you plan your own workload.
Start by thinking about existing pressures. If you're concerned that someone might be at risk of overload, see if you can take some of the pressure off them. This is a simple step to help them improve the quality of their work.
By contrast, if anyone is underworked, it may be in everyone's interest to shorten some deadlines, increase key targets, or add extra responsibilities – but only with clear communication and agreement.
From there, balance the factors that contribute to pressure, so that your people can perform at their best. Remember, too little pressure can be just as stressful as too much!
Try to provide team members with tasks and projects of an appropriate level of complexity, and work to build confidence in the people who need it.
Also, manage any negativity in your team, and train your people so that they have the skills they need to do the jobs they're given. Our article on Training Needs Assessment (TNA) will help you do this. Tools like the Four Dimensions of Relational Work can also help you match tasks to people's personalities and interpersonal skills.
However, bear in mind that you won't always be able to balance the "influencers." Motivate and empower your people so that they can make effective decisions for themselves.
Key Points
The Inverted-U Theory illustrates the relationship between pressure and performance. Also known as the Yerkes-Dodson Law, it explains how to find the optimum level of positive pressure at which people perform at their best. Too much or too little pressure can lead to decreased performance.
Various factors affect how much people react to pressure in different situations. There are "four influencers" that can affect how much pressure people feel:
- Skill Level.
- Personality.
- Trait Anxiety.
- Task Complexity.
The Inverted-U Theory helps you to observe and manage these four factors, aiming for a balance that supports engagement, well-being, and peak performance.
You can use the model by managing these four influencers, and by being aware of how they can positively or negatively influence your people's performance.
*Originator unknown. If you know the originator of the "Four Influencers," please contact us.
References[1] Yerkes, R.M. and Dodson, J.D. (1908). 'The Relation of Strength of Stimulus to Rapidity of Habit-Formation,' Journal of Comparative Neurology and Psychology, 18(5), 459-482. Available
here.



